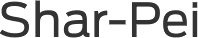In the same way that inbreeding among human populations can increase the frequency of normally rare genes that cause diseases, the selective breeding that created the hundreds of modern dog breeds has put purebred dogs at risk for a large number of health problems, affecting both body and behavior.
In the same way that inbreeding among human populations can increase the frequency of normally rare genes that cause diseases, the selective breeding that created the hundreds of modern dog breeds has put purebred dogs at risk for a large number of health problems, affecting both body and behavior.
Some conditions are directly related to the features breeders have sought to perpetuate among their dogs. As they deliberately manipulated the appearance of dogs to create or accentuate physical characteristics that were considered aesthetically pleasing, like the flat face of a bulldog or low-slung eyelids of a Bloodhound, breeders also created physical disabilities. The excessively wrinkled skin of the Chinese Shar-Pei causes frequent skin infection; Bulldogs and other flat-faced (or brachycephalic) breeds such as the Pekingese have breathing problems because of their set-back noses and shortened air passages; Bloodhounds suffer chronic eye irritation and infection.
 The unnaturally large and small sizes of other breeds encourage different problems. For example, toy and miniature breeds often suffer from dislocating kneecaps and heart problems are more common among small dogs. Giant dogs such as Mastiffs, Saint Bernards, and Great Danes are nearly too big for their own good. Researchers have found a striking correlation between a dog’s large size and a frequency of orthopedic problems like hip dysplasia. Large dogs are often prone to heat prostration because they can’t cool down their bodies (tiny dogs, by contrast, have a hard time staying warm), and because of the massive weight they must support, these breeds are prone to malignant bone tumors in their legs. Meanwhile, the huge head and narrow hips of the Bulldog can necessitate that their pups must be born by Caesarean section.
The unnaturally large and small sizes of other breeds encourage different problems. For example, toy and miniature breeds often suffer from dislocating kneecaps and heart problems are more common among small dogs. Giant dogs such as Mastiffs, Saint Bernards, and Great Danes are nearly too big for their own good. Researchers have found a striking correlation between a dog’s large size and a frequency of orthopedic problems like hip dysplasia. Large dogs are often prone to heat prostration because they can’t cool down their bodies (tiny dogs, by contrast, have a hard time staying warm), and because of the massive weight they must support, these breeds are prone to malignant bone tumors in their legs. Meanwhile, the huge head and narrow hips of the Bulldog can necessitate that their pups must be born by Caesarean section.
YOU MIGHT ALSO LIKE